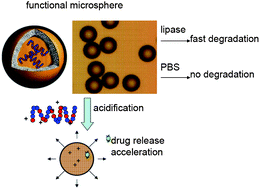
The current study aimed at designing cationic and biodegradable biomaterials with improved biological functionality. We report the enzymatic synthesis, characterization and preliminary biological assessment of a series of novel functionalized poly(ester-co-carbonate)s, namely [poly(ADMC-co-CL)]s containing tertiary amine groups in the backbone. The copolymer compositions agreed very well with the feed ratios of co-monomers, indicating the excellent controllability of the preparation method. Static contact angle measurement revealed that the hydrophilicity of copolymers can be tailored and gradually increased with an increasing ADMC content in copolymers. With respect to the weight loss, in vitrodegradation tests demonstrated the occurrence of lipase-dependent degradation. Copolymers with a higher ADMC content degraded far faster as well. Cell proliferation tests suggested that the incorporation of ADMC in copolymers would considerably promote cell adhesion and proliferation on the polymer surface, indicative of good biocompatibility. As a demonstration of a potential application, poly(ADMC–co-CL) microspheres were fabricated in an attempt to construct a controlled delivery system for the drug ibuprofen. The sustained release of ibuprofen loaded in the copolymers was found to have an evident acceleration in acidic conditions, indicating the pH dependence of such release behavior.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...