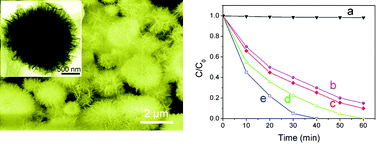
A simple and economical citrate-mediated hydrothermal route has been developed to fabricate three-dimensional hierarchical ZnO microarchitectures with high surface-to-volume ratio and large population of unconventional (0001) surface planes. This complex architecture with flowerlike morphology is assembled by many interleaving nanosheets which have ultrathin thickness of about 5 nm. According to the experimental results, a growth mechanism which involves the assembly of the nanosheets from nanoparticles into flowerlike morphology is proposed. Importantly, this type of hierarchically-structured ZnO displays a strong structure-induced enhancement of photocatalytic performance and exhibits a significantly improved photocatalytic activity in the photodegradation of methyl orange than that of other monomorphological ZnO, such as ZnO nanoparticles, nanorods, and nanosheets. In addition to the large specific surface areas due to ultrathin size of the nanosheet building blocks, the enhanced photocatalytic activity can mainly be ascribed to the special structural feature with good stability and high proportion of active (0001) planes. This work provides an efficient route for the structure-induced enhancement of photocatalytic performance by designing a desirable micro/nanoarchitecture, which could also be extended to synthesize other metal-oxide microarchitectures with superior photocatalytic performance.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...