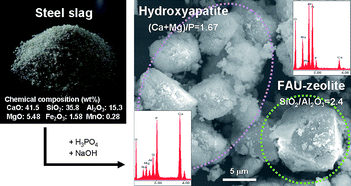
Steel slag is a commercial waste material mainly consisting of SiO2, Al2O3 and CaO, the former two chemicals being major components of zeolites and the latter a major component of hydroxyapatite (HAP). A hydroxyapatite–zeolite composite material (HAP-ZE) was successfully synthesized from steel slag by adding appropriate chemical reagents, H3PO4 and NaOH, viaaging at 363 K for approximately 2 days. The synthesis mechanism and structural properties were clarified by detailed analysis using XRD, FT-IR, SEM, EDX, elemental mapping, and N2 adsorption–desorption measurements. The Ca and Mg components were chemically reacted with phosphate in the early stages of aging, being precipitated as Mg-substituted HAP with (Ca + Mg)/P = 1.67. After 2 days of aging, well-crystallized HAP and faujasite-type zeolite (Na type X-zeolite with SiO2/Al2O3 = 2.4) were separately formed via a non-simultaneous crystallization process. The over-run in aging time led to phase transformation from FAU-zeolite to Pl-zeolite. The minor components in steel slag such as Fe and Mn had little effect on the synthesis of HAP-ZE; however, the inherent SiO2/Al2O3 ratio in steel slag led to a lower yield from the zeolite phase. Furthermore, from the adsorption assessment of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), fatty acid and protein, the HAP-ZE synthesized under optimum conditions was found to have adsorption properties comparable to those of pure zeolite and HAP.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...