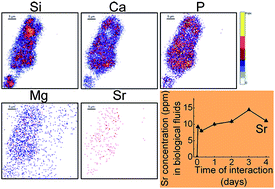
The development of bone tissue regeneration calls for biomaterials able to release biologically active substances in a controlled manner after implantation. In this context, strontium-doped bioactive glasses are of major interest; their key property relies on the increased kinetics of surface reactions, along with the release of critical concentrations of ionic dissolution products capable of stimulating cellular responses. In this paper, we report a complete evaluation of the in vitro reactivity of new SiO2–CaO–SrO and SiO2–CaO–P2O5–SrO bioactive glasses. In contact with simulated acellular physiological fluids, these materials induce the formation of a calcium phosphate surface layer that closely resembles to the biological apatite present in bones. The two most commonly used materials shapes for clinical applications – glass particles and glass bulk – were studied and provide us with concordant results. Compared to strontium-free materials, the dissolution of SiO2–CaO–SrO and SiO2–CaO–P2O5–SrO glasses is reduced. However, the surface layer is more quickly transformed into a bone-like apatite phase, according to the kinetics of evolution of the Ca/P atomic ratio. Evidences of the presence of Sr at the glass/biological fluids interface were obtained, along with the demonstration that this element is released in physiological concentrations into the biological environment. Knowing the well-recognized beneficial effects of strontium on cell activity and bone remodeling, this crucial result gives high hopes for the development of innovative applications based on Sr-doped glasses in the treatment of osteoporosis and tissue engineering.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...