Generation of tunable wavelength lights in core-shell CaWO4 microspheres via co-doping with Na+ and Ln3+ (Ln = Tb, Sm, Dy, Eu)
Abstract
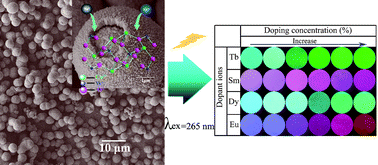
The optimum luminescence and its relevant applications of phosphors are always challenged by the generation of multicolour lights in a single solid with a single-wavelength excitation. In this work, we initiated the preparation of novel core-shell CaWO4 microspheres co-doped with Na+ and Ln3+ (Ln = Tb, Sm, Dy, Eu) and systematically studied their tunable wavelength lights. The core and shell of the microspheres are based on the same materials that crystallized in a tetragonal scheelite structure. The primary particle size for the un-doped microspheres was about 36 nm, while upon doping with Ln3+/Na+, the primary particle became as small as 14–19 nm. This core-shell structure is proved unique in significantly suppressing the energy-loss processes occurring at the

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...