Synthesis, characterization and sensing properties of nano-SnO2 supported on SBA-15 as highly sensitive semiconductor gas sensors
Abstract
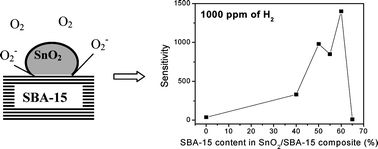
Nanocrystalline SnO2/SBA-15 composites have been successfully synthesized by wet impregnation of SnCl2 using mesoporous structured

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...