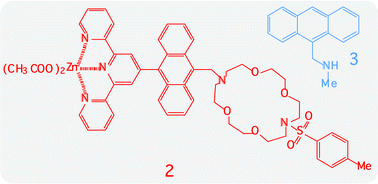
The multicomponent species 1 and 2 (structural formulas shown in Fig. 1), made of diazacrown receptors and anthracene-based chromophores, have been synthesized, together with 3, an already-known species containing the anthracene chromophore and an appended amino group. The absorption spectra and luminescence properties of 1–3 have been studied in acetonitrile solution, both in the absence and presence of protons. All of the compounds exhibit luminescence, the intensity of which is enhanced in the presence of protons, and have the role of inhibiting the reductive electron transfer emission quenching processes operating in non-protonated 1–3. The emission intensity of an equimolar solution of 1 and 3 is increased by proton addition, as expected, however the maximum of the intensity is reached when acid concentration is about 1.5 times higher than those of 1 or 3. This suggests that proton-assisted interaction between 1 and 3 takes place. The equimolar solution of 2 and 3 exhibits two emission features, each one assigned to a component chromophore. Low acid concentration leads to enhancement of the 400 nm emission, related to the species 3, and higher acid concentration allows for enhancement of the 520 nm emission, related to the species 2. A closer observation of the luminescence titration curve, as well as NMR data, indicates that a 2·3 adduct is present even before proton addition, and the adduct is further stabilized by protonation to form 2·H·3.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...