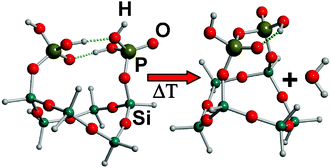
Pyrogenic silica was impregnated with H3PO4, yielding the P-doped silica sample A200/P. Surface features of A200/P were analyzed, as a starting point for the study of more complex silica-based materials such as bioactive glasses (usually made of SiO2, CaO and P2O5). A200/P was analyzed with in situ FTIR spectroscopy, and both the effect of thermal treatments and water adsorption were considered. Surface POH groups were detected in IR spectra, along with the silanol peaks. H-bond interactions occurring between surface OH groups turned out to be much stronger than those usually found on pure silica. By treating the sample at high temperatures (100–700 °C), the peak identified with POH groups red shifted and both the signals of POH and SiOH groups gradually disappeared. Moreover, a new band at ∼1370 cm−1 was formed, which blue shifted with increasing temperature of sample treatment. These features have been rationalized by means of ab initio modelling, using cluster models of possible surface structures. P-containing groups were bound to six-Si-membered siloxane rings, and the structure of the resulting clusters were optimized at the B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p) level. It was shown that POH groups undergo condensation also with either isolated or vicinal silanols, and that the consequent formation of pyrophosphate-like surface species may explain most of the spectral features revealed by IR experiments.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...