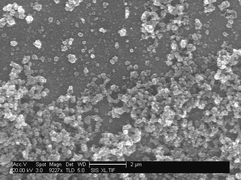
The composition, surface morphology, structure, and electrochemical properties of thin solid films of the polymer, C60–Pd, were studied by Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), and energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF) as well as being examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) with selective area diffraction (SAD) and by cyclic voltammetry (CV), respectively. The C60–Pd films were deposited onto Au or Pt electrodes by electroreductive co-polymerization of C60 and the palladium(II) acetate trimer, [Pd(ac)2]3, in a mixed acetonitrile–toluene (4∶1, v/v) solution of 0.1 M tetra(n-butyl)ammonium perchlorate under multicyclic voltammetry or potentiostatic conditions. The structure and composition of the C60–Pd films were dependent on the relative concentration of the polymer precursors, i.e., C60 and [Pd(ac)2]3, in the solution for electropolymerization. That is, in films grown in solutions with a high [Pd(ac)2]3∶C60 ratio, (–C60–Pd–)n polymeric chains were separated by the Pd nanoclusters. These films were relatively smooth and uniform. In contrast, films electropolymerized in solutions with a low [Pd(ac)2]3∶C60 ratio were rough, porous and much less uniform. The presence of the Pd nanoclusters in the C60–Pd film influenced the electrode processes of probing redox species dissolved in solution. That is, electro-oxidation of an N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-1,4-phenylenediamine (TMPDA) electrochemical redox probe was partially inhibited at the electrode coated by the C60–Pd film with a relatively low Pd nanocluster content. In contrast, electro-oxidation of TMPDA was effectively mediated by the C60–Pd film containing appreciable amounts of dispersed Pd nanoclusters.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...