Abstract
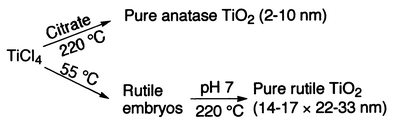
Phase-pure anatase TiO2 nanocrystallites ranging from 2 to 10 nm in size were synthesized directly from a TiCl4 aqueous solution using citric acid as an additive. Citric acid was found to play a decisive role in stabilizing the TiCl4 aqueous solution, leading to the selective formation of the anatase TiO2 nanocrystallites in hydrothermal autoclaving. On the other hand, hydrothermal autoclaving of the rutile TiO2 embryos prepared by room-temperature peptization of the TiCl4 aqueous solution gave rod-like rutile TiO2 nanocrystallites (14–17 × 22–33 nm) under neutral conditions. The presence of KCl or NaCl enhanced the crystal growth of the rutile embryos in the hydrothermal process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...