Hollow fiber supported TiO2 monolithic microextraction combined with capillary HPLC-ICP-MS for sensitive absolute quantification of phosphopeptides†
Abstract
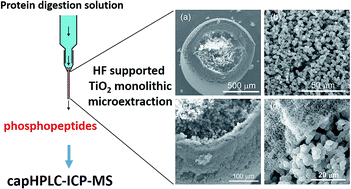
Protein phosphorylation analysis is important for understanding cell regulations. Mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful technique for peptide phosphorylation analysis. However, quantification of low abundance phosphoproteins in a complex mixture of proteins is still a challenge. Here we report the development of hollow fiber (HF) supported TiO2 monolithic microextraction combined with capillary high performance liquid chromatography (capHPLC)-inductively coupled plasma-collision reaction cell (ICP-CRC)-MS for the absolute quantification of phosphopeptides. The membrane pores (∼200 nm) of the HF effectively carry more TiO2 on its surface to enhance the adherence of the TiO2 monolith with the HF. By using β-casein as a model phosphorylated protein, we optimized the HF-supported TiO2 monolithic microextraction towards phosphopeptides. Under the optimal conditions, a 100-fold enrichment factor was obtained and the monoliths can be reused 40 times. By monitoring 31P16O with O2 as a reaction gas in the CRC, polyatomic mass interference at m/z 31 is avoided and a low detection limit (2.9 nM) of phosphorus is achieved. The method of HF-supported TiO2 monolithic microextraction-capHPLC-ICP-MS provided the detection limit for phosphopeptides at the nM level. The proposed method was applied to the quantification of phosphopeptides in milk and milk powder samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...