Calibration-free quantitative analysis of thin-film oxide layers in semiconductors using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)†
Abstract
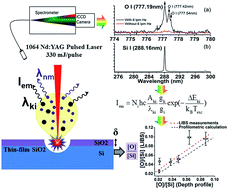
The current largest market share and continually growing industry of the semiconductor manufacturing sector in the US demands rapid and cost-effective quality control and characterization of thin film semiconducting materials. To this end, we demonstrate Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) as a facile and effective analytical tool for rapid process-line characterization of metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) transistors and capacitors. Specifically, we carry out quantitative LIBS analysis on silicon oxide (SiO2) thin-films of various thicknesses grown by high-temperature moisture-free oxidation on industrial-grade Si wafers. The stoichiometric ratios of oxygen to silicon ([O]/[Si]) in various SiO2 films are measured by LIBS analyses using an internal calibration technique. The results are verified against benchmark analyses based on oxide layer thicknesses and laser-induced crater profile topographies from ellipsometry, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and profilometry measurements. The stoichiometric ratios of [O]/[Si] calculated from thickness and profilometry measurements are used to compare with our direct LIBS measurements. Our results indicate good agreement between the LIBS and profilometry calculation results, demonstrating the future capability of LIBS for thin film characterization during their industrial processing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...