Analysis of organic and high dissolved salt content solutions using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry
Abstract
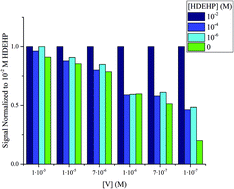
Quantification of analytes present in organic solvents or high salt content aqueous solutions using ICP-OES with minimal to no sample processing is desirable to improve analysis turnaround time and decrease sample cost. This work describes procedures used for Sr, V, and Y quantifications in 1-pentanol, 1-octane, 1-decanol, n-octane, and kerosene, substitute seawater, and NaCl solutions, with concentrations as high as 5 molal, using ICP-OES with a standard nebulizer and spray chamber configuration. The detection limits of analyte in those extreme conditions decrease by less than a factor of ten compared to element quantification in dilute aqueous solution; however, the instrument maintained its normal precision and linearity in response. In dilute HNO3, Sr, V, and Y feature LODs of 4 × 10−2, 4, and 0.2 ng L−1, respectively. A medium of 5 m NaCl shows LODs of 1, 4, and 4 ng L−1 for Sr, V, and Y, respectively. Organic analyses revealed the presence of a number of molecular emissions that occurred during the ionization of carbon; these emissions drastically increased backgrounds in the region around 400 nm. Dodecane solutions were found to require the addition of a metal complexant (we used di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid) to ensure elemental stability of solution. With the addition of the complexant to dodecane solutions, the LODs were 10, 5, and 4 ng L−1 for Sr, V, and Y, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...