A metric for evaluation of the image quality of chemical maps derived from LA-ICP-MS experiments
Abstract
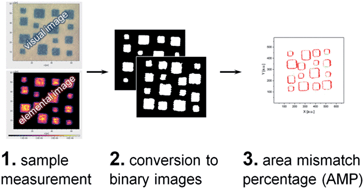
For laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) imaging experiments – as well as other techniques used for elemental or molecular mapping – the accordance of the measured distribution with the actual distribution is of utmost importance to guarantee reliability of the obtained images. In most experiments reported in the past, the experimental conditions have been chosen so that washout effects and signal carry-over are minimized by scanning the sample surface very slowly. Therefore, measurement times become very long and decently resolved images will require acquisition times of several hours up to more than one day. To increase the application range of LA-ICP-MS for imaging it is important to decrease the measurement times, which is best accomplished by increasing the scanning rates. However, depending on the instrumentation, this can lead to blurring and compromised image quality. In this work, we present a metric to compare the measured elemental distribution with their actual distribution based on a sample with visually distinguishable features. This approach allows quantitative determination of the image quality and enables comparison of multiple measurement conditions. This information can be used for method optimization, to get a reasonable tradeoff between image quality and measurement time.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...