Toll-like receptor 2-mediated MAPKs and NF-κB activation requires the GNAO1-dependent pathway in human mast cells
Abstract
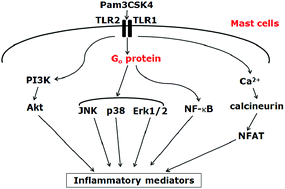
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) expressed on mast cells are essential for effective host defense against a wide variety of pathogens. Previous studies have demonstrated that both TLR2 agonists Pam3CSK4 and PGN stimulated IL-8 release in human mast cells. To determine the molecular basis for this phenomenon, we utilized human mast cell line LAD2 cells. We found that only the release of IL-8 stimulated by Pam3CSK4 was TLR2-mediated, which was confirmed by specific TLR2 shRNA. Heterotrimeric G proteins have been previously implicated in TLR signaling in macrophages and monocytes. In the current study, we showed that PamCSK4 induced the activation of MAPKs, NF-κB, PI3K-Akt and Ca2+-calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascades in LAD2 cells. Go proteins were required for the activation of MAPKs and NF-κB in TLR2 stimulated LAD2 cells. Therefore, the genetic depletion of Gαo proteins also led to the reduction of the release of IL-8 in LAD2 cells. Taken together, the data presented here suggest that TLR2 activation in human mast cells promotes the release of inflammatory mediators via distinct signaling pathways that partially depend on the action of Go proteins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...