Direct conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to biomimetic tendril-like functional carbon helices: a protein friendly host for cytochrome C†
Abstract
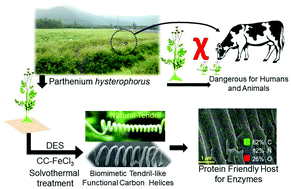
There is sizable interest in the fabrication of carbon helices owing to their uses in several applications. Methods have been developed for the preparation of such carbon helices from nonrenewable hydrocarbons by a metal-catalyzed chemical vapor deposition process. However, such methods require high temperature and toxic gases besides multi-step processes. Herein we report the preparation of tendril-like functional carbon helices (TLFCHs) directly from lignocellulosic biomass using a green solvothermal method employing a deep eutectic solvent as both soft template and catalyst. Under optimized conditions biomimetic helical carbons with fibre widths of 1.5–2.0 μm, coil diameters of 8–10 μm, coil lengths of 30–50 μm and having a high degree of oxygenated functionalities were obtained. Taking advantage of both helicity and in-built chemical functionalities, cytochrome C (Cyt C) was immobilized on the surface of TLFCHs to probe their protein friendly nature. The results demonstrated that TLFCHs showed significant potential as a host for an enzyme without compromising the catalytic activity and thus can be envisaged as a protein friendly biomaterial for facile biocatalysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...