Life cycle assessment of the production of surface-active alkyl polyglycosides from acid-assisted ball-milled wheat straw compared to the conventional production based on corn-starch†
Abstract
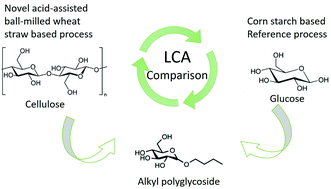
Production of alkyl polyglycosides (APGs) from mechanocatalytic depolymerization of wheat straw is a promising route because of the use of an available bio-based feedstock. This study aims to verify the environmental benefit of this process in comparison with a reference process that produces APGs from corn starch based glucose. A life cycle assessment methodology is used to compare both production routes. The results have shown that the new production route based on wheat straw generates lower environmental impacts compared to the reference process because of the use of wheat straw instead of corn starch based glucose and the energy recovery from the by-product lignin that meets most of the energy demand of the process. The LCA results also show that the production of fatty alcohol dominates the life cycle impact of APGs. Environmental impacts are sensitive to the source of the fatty alcohol (from palm kernel or coconut oil).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...