Imidazolium-based polyionic liquid absorbents for bioproduct recovery
Abstract
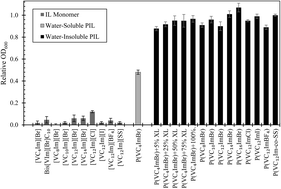
Solid imidazolium-based polyionic liquids (PILs; a class of polyelectrolyte) were synthesized for the absorption of n-butanol and other inhibitory biosynthesis products from dilute aqueous solutions. Conventional hydrogels prepared by cross-linking water-soluble PILs demonstrated biocompatibility with Saccharomyces cerevisiae, successfully eliminating cytotoxicity concerns associated with the IL monomers. However, the cross-linked PILs’ solute absorption capacity and selectivity for butanol relative to water were below the levels likely needed for a viable extractive fermentation process. Uncross-linked PILs bearing long-chain aliphatic substituents also proved to be biocompatible by virtue of their insolubility in water, and delivered significantly improved absorptive performance. Among biocompatible absorbents, these PILs demonstrated some of the highest absorptions of n-butanol and other hydrophilic fermentation products reported to date, with n-butanol partition coefficient (PC) values up to 7.6 and butanol/water selectivity (αb/w) values up to 78. The influence of linear N-alkyl side chain length (C8 to C16) and counter anions (Cl−, Br−, I−, BF4−, co-SS−) on solute partition coefficient, selectivity and physical properties are detailed and discussed. In all, this work demonstrates that polymerization of cytotoxic ILs can successfully yield biocompatible absorbents with excellent absorptive performance for the recovery of hydrophilic bioproducts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...