Glucose promoted facile reduction of azides to amines under aqueous alkaline conditions†
Abstract
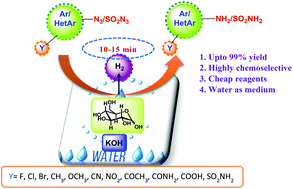
A quick and efficient method for the reduction of azides to amines in water using D-glucose and KOH as green reagents is reported. The protocol is simple, inexpensive, scalable, and can be applied to different aromatic, heteroaromatic and sulphonyl azides. A high level of chemoselectivity is observed for azide reduction in the presence of other reducible functionalities like cyano, nitro, ether, ketone, amide and acid. The reaction gets completed in a short time (5–20 minutes), and furnishes the amines in high yield (85–99%). Unlike conventional hydrogenations, this reduction protocol does not require any metal catalyst, elaborate experimental setup or use of high-pressure equipment.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Green Chemistry Hot Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...