Fabrication of highly dispersed/active ultrafine Pd nanoparticle supported catalysts: a facile solvent-free in situ dispersion/reduction method†
Abstract
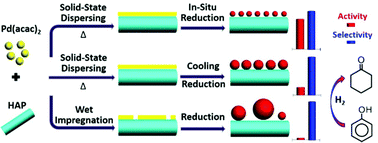
The development of sustainable routes for the synthesis of noble metal supported catalysts is of high importance because of their wide applications on a large scale in the catalysis field. Herein we report a facile solvent-free solid-state dispersion route to fabricate highly dispersed ultrafine palladium nanoparticle supported catalysts. In the first step, a noble metal precursor Pd(acac)2 was dispersed spontaneously by treating the physical mixture of Pd(acac)2 and catalyst support hydroxyapatite (HAP) at 120 °C under a flow of N2. Subsequent H2 reduction results in the formation of two kinds of Pd particles. In situ reduction at 120 °C is essential for preparing highly dispersed Pd nanoparticles (∼1.2 nm, a1Pd/HAP-SSD) and cooling-down reduction leads to the formation of larger Pd nanoparticles (∼4 nm, b1Pd/HAP-SSD). The as-prepared a1Pd/HAP-SSD exhibits higher activity for phenol hydrogenation than b1Pd/HAP-SSD and that obtained by a traditional wet impregnation method, due to the highly dispersed ultrafine Pd0 nanoparticles obtained by in situ dispersion/reduction. Compared with conventional wet chemistry-based methods, the synthesis route in this work simplifies the synthesis process, avoids producing large polluted wastes, and enhances the dispersion of noble metals. This may open a new way to prepare highly dispersed/active noble metal supported catalysts and is also potentially of high importance for the green production of noble metal supported catalysts on a large scale in the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...