Eco-friendly synthesis of indo dyes mediated by a bacterial laccase†
Abstract
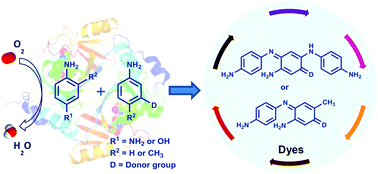
Several aminoindamine and indoaniline dyes were obtained in good to excellent yields (64–98%) by oxidative cross-coupling between 1,4-phenylenediamine (1), 4-aminophenol (2) or 2,5-diaminotoluene (3) and several meta- and meta,para-substituted couplers (4a–j) using a green biocatalyst, the bacterial enzyme CotA-laccase from Bacillus subtilis, in water and under mild conditions of pH and temperature. Our results show that the enzymatic route described represents an efficient and sustainable alternative to the chemical synthesis of indo dyes, with a potentially high impact in the cosmetic and hair dye industries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...