Lignin depolymerization by fungal secretomes and a microbial sink†
Abstract
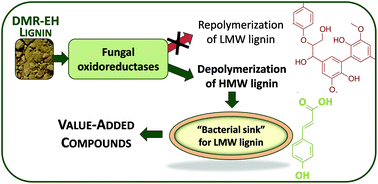
In Nature, powerful oxidative enzymes secreted by white rot fungi and some bacteria catalyze lignin depolymerization and some microbes are able to catabolize the resulting aromatic compounds as carbon and energy sources. Taken together, these two processes offer a potential route for microbial valorization of lignin. However, many challenges remain in realizing this concept, including that oxidative enzymes responsible for lignin depolymerization also catalyze polymerization of low molecular weight (LMW) lignin. Here, multiple basidiomycete secretomes were screened for ligninolytic enzyme activities in the presence of a residual lignin solid stream from a corn stover biorefinery, dubbed DMR-EH (Deacetylation, Mechanical Refining, and Enzymatic Hydrolysis) lignin. Two selected fungal secretomes, with high levels of laccases and peroxidases, were utilized for DMR-EH lignin depolymerization assays. The secretome from Pleurotus eryngii, which exhibited the highest laccase activity, reduced the lignin average molecular weight (Mw) by 63% and 75% at pH 7 compared to the Mw of the control treated at the same conditions and the initial DMR-EH lignin, respectively, and was applied in further depolymerization assays as a function of time. As repolymerization was observed after 3 days of incubation, an aromatic-catabolic microbe (Pseudomonas putida KT2440) was incubated with the fungal secretome and DMR-EH lignin. These experiments demonstrated that the presence of the bacterium enhances lignin depolymerization, likely due to bacterial catabolism of LMW lignin, which may partially prevent repolymerization. In addition, proteomics was also applied to the P. eryngii secretome to identify the enzymes present in the fungal cocktail utilized for the depolymerization assays, which highlighted a significant number of glucose/methanol/choline (GMC) oxidoreductases and laccases. Overall, this study demonstrates that ligninolytic enzymes can be used to partially depolymerize a solid, high lignin content biorefinery stream and that the presence of an aromatic-catabolic bacterium as a “microbial sink” improves the extent of enzymatic lignin depolymerization.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...