Heterogeneous catalytic reaction of microcrystalline cellulose in hydrothermal microwave-assisted decomposition: effect of modified zeolite Beta
Abstract
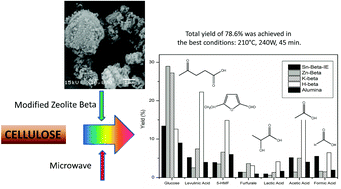
Zeolite Beta, modified with some salts of alkali and alkaline earth metals (K, Zn, Sn), was tested in the hydrothermal heterogeneous catalytic decomposition of microcrystalline cellulose. The reactions were microwave-assisted, where the microwaves were issued by an in situ coaxial applicator. Zeolites were subjected to an ion-exchange process which determines the loss of crystallinity in the following order: Sn-Beta-IE > K-Beta > Zn-Beta > acid form H-Beta. The interaction between zeolites and microwaves was studied by irradiating zeolite powder under constant power and the heating response was in the following order: K-Beta > NH4-Beta > Sn-Beta-IE ≈ Zn-Beta > H-Beta > alumina. These results show that the nature of the counterion strongly affects the absorption of microwaves. The catalytic activity of the different systems on the cellulose decomposition was studied, and resulted in the following order: H-Beta > K-Beta > Zn-Beta > Sn-Beta-IE > alumina, when the reaction medium contained 5 mM HCl. The most active catalyst was the acid zeolite Beta and the identified product distribution under the investigated conditions was (mol yield %): levulinic acid (22.3), glucose (12.1), lactic acid (4.1), formic acid (6.6), 5-(hydroxymethyl) furfural (14.6), acetic acid (15.2) and furfuraldehyde (3.1). The effect of temperature, time and the heterogeneous catalyst reuse (H-Beta) on the yields of different products was investigated. The use of MW radiation with a coaxial applicator instead of conventional heating gave clear advantages in the decrease of the reaction time (45 min) and in terms of yield enhancement (78.6% under the best conditions).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...