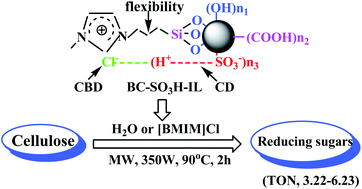
The development of a highly efficient and environmentally friendly process for the hydrolysis of cellulose into reducing sugars could be one of the key technologies for large-scale use of cellulosic biomass in the future. In order to pursue this goal, an ionic liquid (IL)-grafting biochar sulfonic acid catalyst (BC-SO3H-IL) was proposed and conveniently prepared with bamboo powder as a carbon resource and 1-(trimethoxy propyl silane)-3-methyl imidazolium chloride as the IL. Its catalytic performance for the heterogeneous hydrolysis of cellulose and bamboo was checked under microwave irradiation. The designed BC-SO3H-IL catalyst was found to show much higher turnover number (TON, 3.22–6.23 for cellulose and 0.26–2.53 for bamboo) and excellent repeatability for this hydrolysis compared to the corresponding biochar sulfonic acid (BC-SO3H, TON, 1.51–1.81 for cellulose and 0.14–1.33 for bamboo). This is likely to be because the IL groups flexibly joined to biochar sulfonic acid, like cellulose binding domain (CBD) of cellulase, efficiently breaks in the hydrogen bonding network of cellulose molecules. On the other hand, they probably play a harmonious role in the SO3H groups (as a catalysis domain (CD) of cellulase) catalyzing cleavage of the β-1,4 glycosidic bonds of cellulose, as supported by TGA characterization and catalytic reaction results.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...