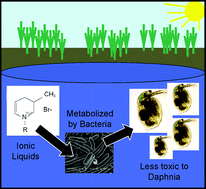
Merging the disciplines of green chemistry, ecotoxicology and ecology to develop environmentally-friendly industrial chemicals represents a significant collaborative challenge. This challenge can be met by extending already-informative standard toxicity and biodegradability assays to include further information about the potential persistence and biotransformation of pollutants in the environment. Development of ionic liquids (ILs) provides an ideal and proactive test system to determine several levels of environmental impact using academically interesting and industrially relevant green chemical prototypes. In this study, we investigated the biodegradability of three ILs, 1-butyl-3-methylpyridinium bromide, 1-hexyl-3-methylpyridinium bromide and 1-octyl-3-methylpyridinium bromide, by activated sludge microbial communities. We determined that all three ILs could be fully mineralized, but that only the octyl-substituted cation could be classified as “readily biodegradable”. We directly examined biodegradation products of the ILs using reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and MS/MS methods, and identified several unique preliminary degradation products. Finally, we determined that IL-biodegradation products were less toxic than the initial compound to a standard aquatic test organism, Daphnia magna, suggesting that biodegradation in an aquatic environment would decrease toxicity hazards associated with the initial compound. This study provides further information about pyridinium IL-biodegradation and guidelines to structure future IL design and research.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...