Selective laccase-mediated oxidation of sugars derivatives†
Abstract
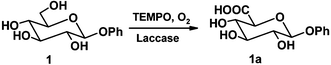
A laccase from Trametes pubescens and the chemical mediator TEMPO have been used to catalyze the regioselective oxidation of the primary hydroxyl groups of sugar derivatives. The efficiency of this system has been initially tested with mono- and

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...