Triterpenoid saponins from the genus Camellia: structures, biological activities, and molecular simulation for structure–activity relationship
Abstract
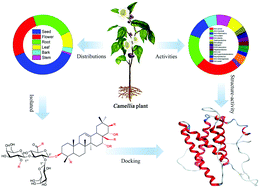
This review summarizes the isolation, chemical identification, and biochemical activities of Camellia triterpenoid saponins, updating a previous review and encompassing all new studies through September 2017. Further, molecular simulations of the interaction between several known cytotoxic oleiferasaponin monomers and Interleukin-6 are discussed, demonstrating that molecular modeling is a convenient method to obtain structure–activity information.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...