Amaranth peptides decreased the activity and expression of cellular tissue factor on LPS activated THP-1 human monocytes
Abstract
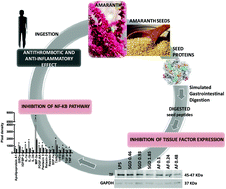
The effect of amaranth peptides on the activity and expression of tissue factor (TF) on THP-1 activated cells was evaluated in vitro. An active anticoagulant peptide fraction (AF) was found to inhibit TF expression (IC50 = 0.39 mg mL−1) and activity. Immunocytochemical fluorescence confocal microscopy analysis showed that treated monocytes decreased TF membrane translocation by 49.0% and increased two-fold in nuclei compared to a positive control, indicating a decrease of active TF to initiate the coagulation cascade. Moreover, a cytokine array suggested that the AF mechanism of action implied the inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. Expression of MIP-3α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-1α, TARC, pentaxin 3, and PDGF-AA cytokines was highly suppressed by AF peptides, producing reductions of 78.8%, 61.8%, 54.1%, 42.6%, 37.9% and 37.8%, respectively, compared to a positive control. The results suggest a potential mechanism for the antithrombotic and anti-inflammatory effect of AF, by showing that amaranth peptides play a negative feedback regulatory role over the NF-κB pathway. In this research, we link for the first time the immunomodulatory activity of amaranth peptides with the inhibition of TF expression and therefore their antithrombotic potential.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...