Tailoring of structured hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-stabilized emulsions for encapsulation of nobiletin: modification of the oil and aqueous phases†
Abstract
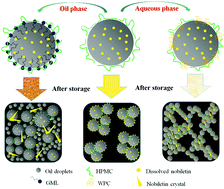
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)-stabilized emulsions were produced and their structure was further modified by altering the oil (glycerol monolaurate, GML) and aqueous (whey protein concentrate, WPC) phases. Then, the encapsulation and release of nobiletin were evaluated. HPMC (3%) could efficiently stabilize the oil droplets with a particle size around 370 nm. When HPMC was the emulsifier, the stabilization time of nobiletin in the emulsion was prolonged, but its encapsulation amount was still maintained around 4.5 mg g−1. Nobiletin crystals were found to adsorb on the interface of oil droplets. The addition of GML and WPC changed the microstructure of HPMC-stabilized emulsions. Both of them enhanced the encapsulation efficiency and storage stability of nobiletin. Nobiletin crystals became softer and shorter. After modification, nobiletin was stable for one week at a level of 7.5 mg g−1. The bioaccessibility of nobiletin was modulated in the presence of GML and WPC. The results demonstrate that the structure of emulsion-based delivery systems affects the encapsulation and delivery of hydrophobic components.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...