Black tea increases hypertonic stress resistance in C. elegans†
Abstract
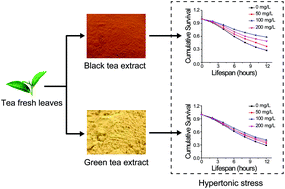
Here we identified that BTE (black tea extract), within the studied concentration range, is more effective than GTE (green tea extract) in protecting C. elegans against hypertonic stress, by enhancing survival after exposure to various salts, and alleviating suffered motility loss and body shrinkage. The mechanism of such protection may be due to the ability of black tea to induce the conserved WNK/GCK signaling pathway and down-regulation of the expression levels of nlp-29. Intriguingly, black tea does not relieve hypertonicity-induced protein damage. The findings implicate the potential health benefits of black tea consumed worldwide.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...