Probiotic attributes and prevention of LPS-induced pro-inflammatory stress in RAW264.7 macrophages and human intestinal epithelial cell line (Caco-2) by newly isolated Weissella cibaria strains†
Abstract
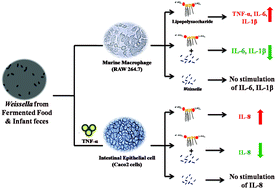
Probiotic lactic acid bacteria are known to modulate gut associated immune responses. Not many studies have reported on the role of Weissella species in preventing lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced proinflammatory stress in murine macrophages as well as in human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). Therefore, the present study was taken up to evaluate the probiotic attributes of four newly isolated Weissella strains (two each from fermented dosa batter and a human infant faecal sample); these attributes are cholesterol reduction, adhesion to Caco-2 cells and mucin and their ability to prevent LPS-induced nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokine (IL-6, IL-1β and TNFα) production by the murine macrophages and IL-8 production by the human epithelial cells. Reduction in LPS induced pro-inflammatory stress was compared with a well-studied probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. The results suggested that the strains were tolerant to gastric conditions (pH 3.0) and bile salts. In addition, the strains exhibited moderate cell surface hydrophobicity, cholesterol reduction and adhesion to Caco-2 cells and gastric mucin. All the strains could prevent LPS-induced nitric oxide and IL-6 production in murine macrophages, while strain 28 alone prevented IL-1β production. All the strains could prevent IL-8 production by the human epithelial cells. The present study led to the first line selection of W. cibaria 28 as a putative strain for future studies as it showed adhesion to Caco-2 cells and gastric mucin and cholesterol reduction besides preventing LPS-induced pro-inflammatory stress in macrophages and in human colonic epithelial cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...