Leaf parts from Greek artichoke genotypes as a good source of bioactive compounds and antioxidants
Abstract
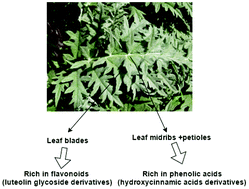
Globe artichoke is an important vegetable in the Mediterranean diet. However, the marketable part of the plant constitutes a small portion of its total crop biomass and large amounts of waste are produced during its cultivation. In this study, the phenolic compound content and composition and the antioxidant activity of leaf parts [blades (SLB), petioles and midribs (SPM)] from various Greek artichoke genotypes were evaluated. The results showed significant variation in antioxidant activities and bioactive compound contents between the studied genotypes, with the leaf blades of most of the genotypes having a high content of flavonoids (mainly luteolin glycoside derivatives), which ranged between 49 and 78% of total phenolic compounds (TPC). In contrast, in petioles and midribs phenolic acids (mainly hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives) were the main phenolic compounds, ranging between 64 and 76% of TPC. The antioxidant activity of blades was significantly higher than that of petiole and midribs for all the genotypes and the tested assays. In conclusion, artichoke leaves (blades, petioles and midribs) of the studied genotypes showed different bioactive compound profiles and significant antioxidant properties, and could be further used in the food and nutraceuticals industries as a cheap source of phenolic compounds and antioxidants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...