Aqueous extracts from asparagus stems prevent memory impairments in scopolamine-treated mice
Abstract
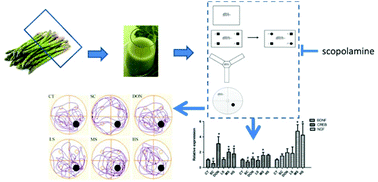
Aqueous extracts from Asparagus officinalis L. stems (AEAS) are rich in polysaccharides, gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA), and steroidal saponin. This study was designed to investigate the effects of AEAS on learning, memory, and acetylcholinesterase-related activity in a scopolamine-induced model of amnesia. Sixty ICR mice were randomly divided into 6 groups (n = 10) including the control group (CT), scopolamine group (SC), donepezil group (DON), low, medium, and high dose groups of AEAS (LS, MS, HS; 1.6 mL kg−1, 8 mL kg−1, 16 mL kg−1). The results showed that 8 mL kg−1 of AEAS used in this study significantly reversed scopolamine-induced cognitive impairments in mice in the novel object recognition test (P < 0.05) and the Y-maze test (P < 0.05), and also improved the latency to escape in the Morris water maze test (P < 0.05). Moreover, it significantly increased acetylcholine and inhibited acetylcholinesterase activity in the hippocampus, which was directly related to the reduction in learning and memory impairments. It also reversed scopolamine-induced reduction in the hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) mRNA expression. AEAS protected against scopolamine-induced memory deficits. In conclusion, AEAS protected learning and memory function in mice by enhancing the activity of the cholinergic nervous system, and increasing BDNF and CREB expression. This suggests that AEAS has the potential to prevent cognitive impairments in age-related diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...