Beneficial effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on spermatogenesis by improving antioxidant activity and inhibiting apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male mice
Abstract
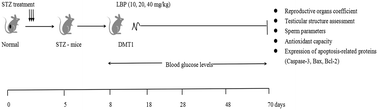
Spermatogenic dysfunction is one of the major secondary complications of diabetes. L. barbarum polysaccharide (LBP) has long been considered to possess anti-apoptotic activities and antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and fertility-enhancing properties in traditional medical practices in China. The aim of the current study was to seek out scientific evidence to determine if LBP also contributes to the recovery from spermatogenic dysfunction in diabetic individuals. We investigated whether the oral administration of LBP in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced type-1 diabetic male mice would reverse spermatogenic dysfunction and improve histological damage in testes. After the oral administration of LBP (10, 20 or 40 mg kg−1, respectively), sildenafil citrate (5 mg kg−1) or saline for 62 consecutive days, the sperm parameters were analyzed. Macroscopic and microscopic changes in the reproductive organs, including their weight, and photomicroscope and electronmicroscope images were also assessed. In addition, the antioxidant capacity and levels of malondialdehyde in the testes were determined according to the instructions provided with the assay kits and the expression of the apoptosis-related proteins, Caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2, in the testes was analyzed using western-blot analysis. LBP treatment of diabetic mice considerably recovered the sperm parameters, increased the weight of the reproductive organs, ameliorated their histological appearance and increased antioxidant enzyme activity to different degrees. Moreover, our data also showed a marked decrease in Caspase-3 expression and an increase in the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax 43 after LBP administration (40 mg kg−1) when compared to the diabetic group. These results demonstrate that LBP exerts protective effects on diabetes induced male spermatogenic dysfunction, which is likely to be mediated through increasing antioxidant enzyme activities and inhibiting cell death.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...