Redox chemistry of the molecular interactions between tea catechins and human serum proteins under simulated hyperglycemic conditions
Abstract
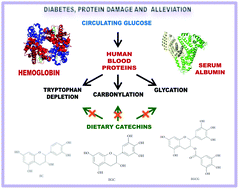
Carbonylation is an irreversible modification in oxidized proteins that has been directly related to a number of health disorders including Type 2 diabetes. Dietary antioxidants have been proposed to counteract the oxidative stress occurring under hyperglycemic conditions. An understanding of the nature and consequences of the molecular interactions between phytochemicals and human plasma proteins is of utmost scientific interest. Three tea catechins namely epicatechin (EC), epigallocatechin (EGC) and epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) were tested for (i) their affinity to bind to human serum albumin (HSA) and human hemoglobin (HH) and (ii) their ability to inhibit tryptophan (Trp) depletion and for the formation of specific protein carbonyls and pentosidine in the aforementioned proteins. Both proteins (20 mg mL−1) were allowed to react with postprandial plasmatic concentrations of the catechins (EC: 0.7 μM, EGC: 1.8 μM, and EGCG: 0.7 μM) under simulated hyperglycemic conditions (12 mM glucose/0.2 mM Fe3+/37 °C/10 days). The three catechins were able to inhibit Trp oxidation and protein carbonylation in both plasma proteins. Some anti-glycation properties were linked to their binding affinities. The molecular interactions reported in the present study may explain the alleged beneficial effects of tea catechins against the redox impairment linked to hyperglycemic conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...