Tenuigenin exhibits anti-inflammatory activity via inhibiting MAPK and NF-κB and inducing Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in macrophages
Abstract
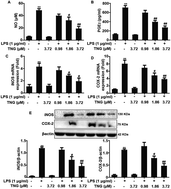
Tenuigenin (TNG), isolated from the root of the Chinese herb Polygala tenuifolia, possesses various biological and pharmacological activities, including anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation activities. In this study, we aimed to further investigate whether its anti-inflammatory activity is associated with the inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Our results showed that TNG treatment dramatically reduced prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and NO production, decreased iNOS and COX-2 gene expression, inhibited JNK1/2, ERK1/2, p38 and NF-κB (p65) phosphorylation, and blocked IκBα phosphorylation and degradation. Further studies revealed that TNG dramatically up-regulated heme oxygenase (HO)-1 and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) expression, which was related to the induction of Nrf2 nuclear translocation and decreased Keap1 protein expression. Additionally, treatment with JNK1/2, ERK1/2 or p38 inhibitors had no effect on the TNG-induced HO-1 protein expression. Furthermore, the LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression levels were inhibited by TNG, which was partially reversed by the HO-1-siRNA and HO-1 inhibitors. Together, these results showed that TNG's anti-inflammatory activity is related to the inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 expression via down-regulation of the MAPK and NF-κB, and up-regulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...