The nutritional composition and anti-hypertensive activity on spontaneously hypertensive rats of sipuncula Phascolosoma esculenta
Abstract
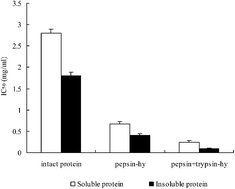
Recent studies have investigated anti-hypertensive peptides derived from natural food products. In this work, we focus on Phascolosoma esculenta as a resource of anti-hypertensive peptides, which is also a seafood with high nutritive value. Compared with FAO/WHO requirements, P. esculenta was confirmed to contain high contents of amino acids and minerals. To investigate the anti-hypertensive activity of P. esculenta, water-soluble and insoluble proteins were extracted and hydrolysed by pepsin and trypsin, respectively. The hydrolysates of water-soluble proteins derived by pepsin and pepsin–trypsin exhibited angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 0.67 and 0.24 mg ml−1, respectively, and those of water-insoluble proteins presented IC50 values of 0.4 and 0.1 mg ml−1, respectively. Experiments on ‘spontaneously hypertensive rats’ (SHRs) were carried out to test the anti-hypertension activity in vivo, which confirmed that the hydrolysates played a significant role in reducing both diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and systolic blood pressure (SBP). Consistently, the in vivo anti-hypertensive activity of the hydrolysis products of pepsin and trypsin used together was also higher than that by using pepsin hydrolysis products alone. As stated in both sets of results, we believe that P. esculenta is an excellent resource of antihypertensive peptides and warrants further investigation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...