Pasta supplemented with isolated lupin protein fractions reduces body weight gain and food intake of rats and decreases plasma glucose concentration upon glucose overload trial
Abstract
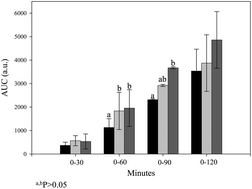
The supplementation of foods with biologically active compounds can be a powerful approach for improving diet and well being. In this study we separately included in pasta matrices a concentrate of γ-conglutin, a glucose-lowering protein from Lupinus albus seeds, an isolate of the other main lupin storage proteins and ovalbumin, at a ratio corresponding to 125 mg of pure protein in 100 g of pasta. With these products we fed rats made hyperglycaemic, for 3 weeks. Among the most relevant changes measured in body and blood parameters were: (i) a significant reduction in food intake of rats fed γ-conglutin concentrate supplemented pasta and a significant limitation in the body weight increase in rats fed α, β and δ-conglutin isolate supplemented pasta, while the food conversion indices were unchanged; (ii) a reduction in glycaemia upon glucose overload trial, especially in the γ-conglutin concentrate supplemented pasta fed animals, at a dose of 45 mg per kg body weight. The correlations among the measured parameters are discussed. Overall, the results evidence the potentiality of supplementing traditional foods with exogenous nutraceutical seed proteins to control body weight gain and glycaemia.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...