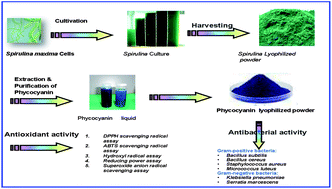
In this study, Spirulina maxima (SM) has been selected following preliminary investigations, for cultivation in either normal (0.02 M) or stress (0.1 M) NaCl medium (Zarrouk) under room conditions to evaluate the possibility of increasing the total phycobiliprotein content (TPC) and their chemical constituents: C-phycocyanin (C-PC), allophycocyanin (APC) and phycoerthrin (PE). TPC material was separated, purified and characterized by various spectroscopic techniques (UV-Vis and IR spectra). The antioxidant activity against free radicals of DPPH, ABTS, superoxide (˙−O2), hydroxy (˙OH) and reducing power potential were determined. Results indicated a highly significant correlation between increased TPC content in SM cells and the increasing concentration of NaCl in medium, and its chemical constituents were significantly different (P > 0.05). TPC of SM (grown in stress NaCl) containing high amounts of C-PC groups, showed strong antioxidant activity compared with ascorbic acid (standard antioxidant). Although, it activity against different free radicals were found to be variable and dose-dependent. Moreover, the TPC showed lower antimicrobial activity (MIC values in the range of 250–300 μg mL−1) than that of chloramphinicol (30 μg mL−1, reference antimicrobial). Therefore, Spirulina maxima could be cultivated in a salinated open pond, and considered as highly healthy foods and source of natural pigments.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...