Influence of nanoparticle inclusions on the performance of reverse osmosis membranes
Abstract
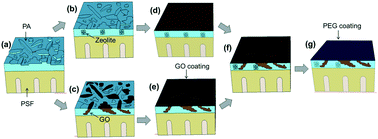
With the rising demand for sustainable production of fresh water from saline sources, various types of water desalination membranes have been reported. Recent papers have used nanomaterials to improve water flux and salt rejection. Herein, we report comparative studies about the performance of reverse osmosis membranes whose selective layers were modified by embedding two different types of hydrophilic filler particles for higher water permeability as well as coating the surface for better antifouling performance. To evaluate the influence of the fillers and coating on the membrane performance, seven different types of samples were prepared and tested by altering one parameter at a time for systematic studies. When zeolite and graphene oxide were embedded in the selective layer made of polyamide, the water permeability was greatly improved. Graphene oxide and polyethylene glycol layers coated on the selective layer resulted in better antifouling performances. We observed a water permeability of 13.2 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 at 96% salt rejection and 15.9 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 at 94.3% salt rejection, which are better than or comparable to those of the unmodified polyamide membranes and superior to many other advanced membranes in the literature. Our systematic and comparative studies identified the influence of each nanoparticle and its concentration on the membrane performances (water permeability and salt rejection) and characteristics (surface roughness and hydrophilicity), which will be of great help to select the nanomaterials and their concentrations for better membrane performances.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...