Gas-permeable hydrophobic tubular membranes for ammonia recovery in bio-electrochemical systems
Abstract
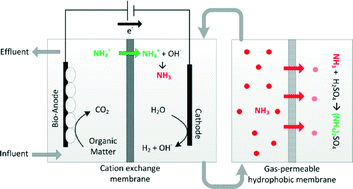
The application of a gas-permeable hydrophobic tubular membrane in bio-electrochemical systems enables efficient recovery of ammonia (NH3) from their cathode compartments. Due to a hydrogen evolution reaction at the cathode, no chemical addition was required to increase the pH for continuous NH3 recovery from wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...