Curation of datasets, assessment of their quality and completeness, and nanoSAR classification model development for metallic nanoparticles†
Abstract
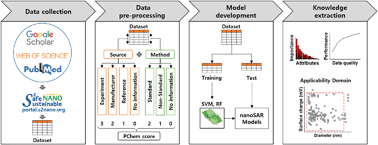
Applications of machine learning techniques for the prediction of nanotoxicity are expected to reduce time and cost of nanosafety assessments. However, due to the rapid increases in literature data quantity and heterogeneity on nanomaterials, efficient screening of data based on their quality and completeness are becoming more important for the development of reliable nanostructure–activity relationship (nanoSAR) models. Herein, we have curated a nanosafety dataset of metallic NPs, with 2005 rows and 31 columns extracted from literature data mining of 63 published articles and gap filling by adapting data from manufacturer specification or references on the same nanomaterials. By using PChem scores based on physicochemical data quality and completeness, five datasets with different qualities and degrees of completeness were generated and used for the development of toxicity classification models of metallic NPs. Comparisons of these models, built with support vector machine and random forest algorithms, confirmed us that the datasets with higher quality and completeness (i.e., higher PChem score) produced better performing nanoSAR models than those with lower PChem scores. Further analysis of relative attribute importance showed that the physicochemical properties, core size and surface charge, and the experimental conditions of toxicity assays, dose and cell lines, are the four most important attributes to the toxicity of metallic NPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...