Synthesis of three crystalline forms of Al2O3 featuring rod-like fibers and their effect on the gaseous degradation of 1-chloronaphthalene†
Abstract
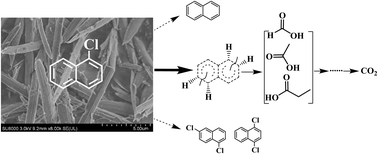
Three crystalline forms of Al2O3 featuring rod-like fibers are synthesized, to perform the gaseous degradation of 1-chloronaphthalene (CN-1), a model compound. The degradation efficiency (DE) decreases as follows: micro/nano-γ-Al2O3 > micro/nano-η-Al2O3 > regular α-Al2O3. The high DE of 92.2% attained over γ-Al2O3 is attributed to its specific defective spinel structure, resulting in its large surface area and pore volume, large amounts of surface-adsorbed oxygen species, and Brønsted and Lewis acid sites. The degradation products, naphthalene and 1,4/1,6-dichloronaphthalene (DiCN), with yield ratios of 7.3–13.3, are detected, indicating the occurrence of hydrodechlorination and side chlorination reactions. 1,6-DiCN is believed to be the most favored DiCN isomer product based on the calculated ΔHr and ΔGr. However, the percentage values of intermediates formed via these two reactions, in the degradation of CN-1, are 9.1%, 4.5% and 4.4%, over α-, η- and γ-Al2O3, respectively. The oxidative degradation pathway possibly dominantly occurs especially over micro/nano-γ-Al2O3 with oxidative species such as O2−, O− and O2−, following the Mars–van Krevelen mechanism. Oxidation intermediates containing –CH2–, –CH3, and C–O groups are produced, which can be subsequently oxidized to low-molecular-weight products, such as formic, acetic and propanoic acids, and eventually completely oxidized to CO2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...