Molecular mechanisms of maize seedling response to La2O3 NP exposure: water uptake, aquaporin gene expression and signal transduction†
Abstract
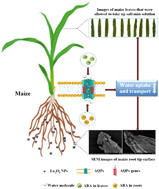
Due to its increasing demands for use in medical, industrial, and agricultural products, concerns over the risks of lanthanum oxide nanoparticle (La2O3 NP) exposure have increased. As the dominant primary producers in terrestrial ecosystems, higher plants represent a sensitive receptor of concern but the mechanisms of La2O3 NP phytotoxicity remain unknown. In the present study, maize was selected as a model plant and the mechanisms underlying growth inhibition and reduced water uptake upon hydroponic exposure to La2O3 NPs (50–500 mg L−1) were investigated. The root and shoot abscisic acid (ABA) content was increased significantly (1.31–7.47 fold) upon exposure to 50 mg L−1 and 250 mg L−1 La2O3 NPs at 36 h and 72 h. The relative expressions of most aquaporin (AQP) genes in both roots and shoots were downregulated after 72 h and 144 h of 50 mg L−1 and 250 mg L−1 La2O3 NP exposure. Compared to the control, the expression level of PIP2;5 at 72 h was decreased by 93.28% in roots exposed to 250 mg L−1; the expression level of PIP1;2 was decreased by 89.85% at 144 h in shoots exposed to 250 mg L−1 La2O3 NPs. The downregulation of AQP genes led to the reduction of water uptake, subsequently causing significant growth inhibition. For example, upon exposure to 50 mg L−1 La2O3 NPs maize root biomass was decreased by 22.73% at 144 h as compared to the control. Additionally, root morphology was severely altered upon exposure to 250 mg L−1 La2O3 NPs as determined by root thickness, length, and surface integrity. To our knowledge, this is the first study evaluating the molecular basis of plant response to La2O3 NP exposure as measured by signal transduction, gene expression and water uptake.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...