Impacts of nanomaterials on bacterial quorum sensing: differential effects on different signals†
Abstract
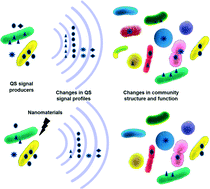
Using Pseudomonas syringae and Pantoea stewartii as model organisms, we quantified the influence of silver nanoparticles and single-wall carbon nanotubes on the production of different acylated homoserine lactones for quorum sensing (QS). This study reports for the first time on differential effects exhibited by nanomaterials on different QS signals.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...