The fate and transformation of tetrabromobisphenol A in natural waters, mediated by oxidoreductase enzymes†
Abstract
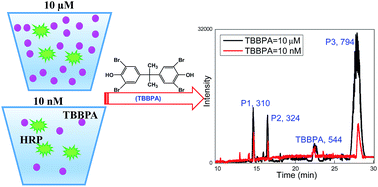
In this study, we examined the fate and transformation of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA), mediated by the representative oxidoreductases (laccase and horseradish peroxidase (HRP)) in natural waters. Both enzymes could readily degrade TBBPA at environmentally relevant concentrations (e.g., 10 nmol L−1) in natural waters. After 2 hour treatment, 0.5–25% and 35–65% of TBBPA were degraded in municipal wastewater and natural surface waters by a laccase or HRP-catalyzed reaction, respectively. Enzyme kinetics evaluations indicated that the kCAT/KM ratio of HRP (1.01 μM−1 s−1) was much higher than that of laccase (0.032 μM−1 s−1) for TBBPA degradation, suggesting that the catalytic performance of HRP towards TBBPA was more efficient than that of laccase. The effects of pH and organic matter on the enzymatic degradation efficiency were explored. Organic matter in the water inhibited the enzymatic degradation efficiency and the degree of inhibition was proportional to the UV254 values of water. Product identification indicated that the product distribution of TBBPA at low concentration (10 nmol L−1) was similar to that of TBBPA at high concentration (10 μmol L−1). The degradation intermediates underwent further enzymatic reaction to yield higher molecular weight secondary products. Toxicity assessment showed that TBBPA toxicity was effectively eliminated by the oxidoreductase-catalyzed reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...