Nitrate pollution and its transfer in surface water and groundwater in irrigated areas: a case study of the Piedmont of South Taihang Mountains, China†
Abstract
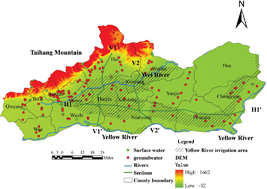
Irrigation projects have diverted water from the lower reaches of the Yellow River in China for more than 50 years and are unique in the world. This study investigated the effect of irrigation practices on the transfer and regional migration mechanisms of nitrate (NO3−) in surface water and groundwater in a Yellow River alluvial fan. Hydrochemical indices (EC, pH, Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl−, SO42−, and HCO3−) and stable isotopic composition (δ18O and δD) were determined for samples. Correlation analysis and principal component analysis (PCA) were performed to identify the sources of water constituents. Kriging was employed to simulate the spatial diffusion of NO3− and stable isotopes. Our results demonstrated that the groundwater exhibited more complex saline conditions than the surface water, likely resulting from alkaline conditions and lixiviation. NO3− was detected in all samples, 87.0% of which were influenced by anthropogenic activity. The NO3− pollution in groundwater was more serious than the common groundwater irrigation areas in the North China Plain (NCP), and was also slightly higher than that in surface water in the study area, but this was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). In addition, the groundwater sites with higher NO3− concentrations did not overlap with the spatial distribution of fertilizer consumption, especially in the central and western parts of the study area. NO3− distributions along the hydrogeological cross-sections were related to the groundwater flow system. Hydrochemical and environmental isotopic evidences indicate that surface water-groundwater interactions influence the spatial distribution of NO3− in the Piedmont of South Taihang Mountains.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...