Effectiveness assessment of soil conservation measures in reducing soil erosion in Baiquan County of Northeastern China by using 137Cs techniques
Abstract
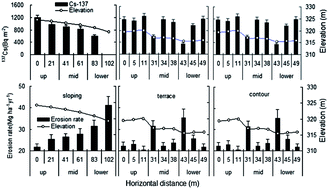
Accelerated soil erosion is considered as a major land degradation process resulting in increased sediment production and sediment-associated nutrient inputs to the rivers. Over the last decade, several soil conservation programs for erosion control have been conducted throughout Northeastern China. Reliable information on soil erosion rates is an essential prerequisite to assess the effectiveness of soil conservation measures. A study was carried out in Baiquan County of Northeastern China to assess the effectiveness of soil conservation measures in reducing soil erosion using the 137Cs tracer technique and related techniques. This study reports the use of 137Cs measurements to quantify medium-term soil erosion rates in traditional slope farmland, contour cropping farmland and terrace farmland in the Dingjiagou catchment and the Xingsheng catchment of Baiquan County. The 137Cs reference inventory of 2532 ± 670 Bq m−2 was determined. Based on the principle of the 137Cs tracer technique, soil erosion rates were estimated. The results showed that severe erosion on traditional slope farmland is the dominant soil erosion process in the area. The terrace measure reduced soil erosion rates by 16% for the entire slope. Typical net soil erosion rates are estimated to be 28.97 Mg per hectare per year for traditional slope farmland and 25.04 Mg per hectare per year for terrace farmland in the Dingjiagou catchment. In contrast to traditional slope farmland with a soil erosion rate of 34.65 Mg per hectare per year, contour cultivation reduced the soil erosion rate by 53% resulting in a soil erosion rate of 22.58 Mg per hectare per year in the Xingsheng catchment. These results indicated that soil losses can be controlled by changing tillage practices from the traditional slope farmland cultivation to the terrace or contour cultivation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...