Mercury wet deposition in the eastern United States: characteristics and scavenging ratios†
Abstract
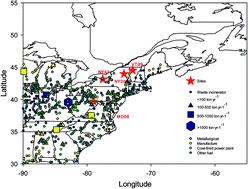
Wet deposition is an important atmospheric mercury (Hg) pathway between air and terrestrial ecosystems. It is measured at numerous locations in the United States (U. S.) as part of the Mercury Deposition Network (MDN). The annual Hg wet deposition flux in 2009 at four locations in the northeastern U. S. (MDN sites MD08, VT99, NY20, and NY43) ranged from 6.4 to 13.4 μg per m2 year which is higher than modeled reactive Hg (RM) dry deposition for this region. The highest ambient RM concentrations were seen at MD08, which is closest to significant anthropogenic sources; however, the volume-weighted mean Hg concentrations in precipitation were similar at these four sites. Mass based scavenging ratios (SC) of RM ranged from 1700 to 4500. Differences in SCs were likely a result of differences in meteorological conditions, the forms of RM in the atmosphere, vertical concentration variations, and measurement uncertainties, including precipitation depth and RM concentrations. RM SCs were higher than those reported for other soluble species. Multiple linear regression suggests that gaseous oxidized Hg is responsible for the majority of the scavenged RM.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...