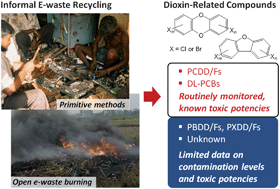
E-waste recycling using uncontrolled processes is a major source of dioxin-related compounds (DRCs), including not only the regulated polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (DL-PCBs) but also non-regulated brominated and mixed halogenated compounds (PBDD/Fs and PXDD/Fs). Various studies at informal e-waste recycling sites (EWRSs) in Asian developing countries found the soil contamination levels of PCDD/Fs from tens to ten thousand picogram TCDD-equivalents (TEQ) per gram and those of DL-PCBs up to hundreds of picogram TEQ per gram. The air concentration of PCDD/Fs was reported as high as 50 pg TEQ per m3 in Guiyu, the largest Chinese EWRS. Non-regulated compounds also contributed substantially to the total DL toxicity of the DRC mixtures from e-waste, as evidenced by the high TEQ levels estimated for the currently identifiable PBDD/Fs as well as the large portion of unexplained bioassay-derived TEQ levels in soils/dusts from EWRSs. Considering the high exposure levels estimated for EWRS residents, especially children, comprehensive emission inventories of DRCs from informal e-waste recycling, the identities and toxic potencies of unidentified DRCs released, and their impacts on human health need to be investigated in future studies.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...